
Matjaz Kunaver
National Institute of Chemistry, Slovenia
Title: Biomass waste – A source of raw materials and nanocellulose
Biography
Biography: Matjaz Kunaver
Abstract

 Cellulose containing Biomass represents an immense and renewable source for the production of bio-fuels and valuable chemicals. A little amount of this is used in industry and the remaining is leftover in huge quantities. Much effort has been devoted in converting these types of biomass into useful industrial and commercially viable products. In recent years, some effective processes have been found, such as thermochemical conversion producing several new products from these renewable resources. An overview of such applications and methods will be presented in this contribution. One of possibilities of converting biomass is the liquefaction. During liquefaction reaction, lignocellulosic components are depolymerized to low molecular mass compounds with high reactivity, high hydroxyl group content and can be used in many useful applications. A high energy ultrasound or microwaves can be used as an energy source to speed up the liquefaction process. The liquefied biomass was used as a feedstock in the synthesis of polyesters, polyurethane foams and adhesives. The same liquefaction process was used for the isolation of the nanocrystalline cellulose from biomass. The method is a novelty and a model procedure for NCC isolation from different natural cellulosic sources with high yields and with high crystallinity index. The process of
Cellulose containing Biomass represents an immense and renewable source for the production of bio-fuels and valuable chemicals. A little amount of this is used in industry and the remaining is leftover in huge quantities. Much effort has been devoted in converting these types of biomass into useful industrial and commercially viable products. In recent years, some effective processes have been found, such as thermochemical conversion producing several new products from these renewable resources. An overview of such applications and methods will be presented in this contribution. One of possibilities of converting biomass is the liquefaction. During liquefaction reaction, lignocellulosic components are depolymerized to low molecular mass compounds with high reactivity, high hydroxyl group content and can be used in many useful applications. A high energy ultrasound or microwaves can be used as an energy source to speed up the liquefaction process. The liquefied biomass was used as a feedstock in the synthesis of polyesters, polyurethane foams and adhesives. The same liquefaction process was used for the isolation of the nanocrystalline cellulose from biomass. The method is a novelty and a model procedure for NCC isolation from different natural cellulosic sources with high yields and with high crystallinity index. The process of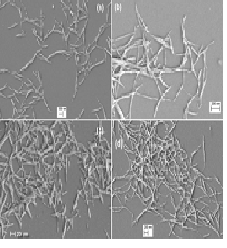

[1] Kunaver M, JasiukaitytÄ— E, ÄŒuk N (2012) Ultrasonically assisted liquefaction of lignocellulosic materials Bioresource Technology 103:360-366
[2] Kunaver M, Anžlovar A, Žagar E (2016) The fast and effective isolation of nanocellulose from selected cellulosic feedstocks Carbohydrate polymers 148:251-256
[3] Khalil H P S A, Bhat A H, Yusra A F I (2012) green composites from sustainable cellulose nanofibrils: a review Carbohydrate Polymers 87: 963-979
[4] Fan J, Li Y Maximazing the yield of nanocrystalline cellulose from cotton pulp fiber (2012) Carbohydrate Polymer 88:1184-1188
[5] Texeira et al. (2010) Cellulose nanofibers from white and naturally colored cotton fibers Cellulose 17: 595-606

